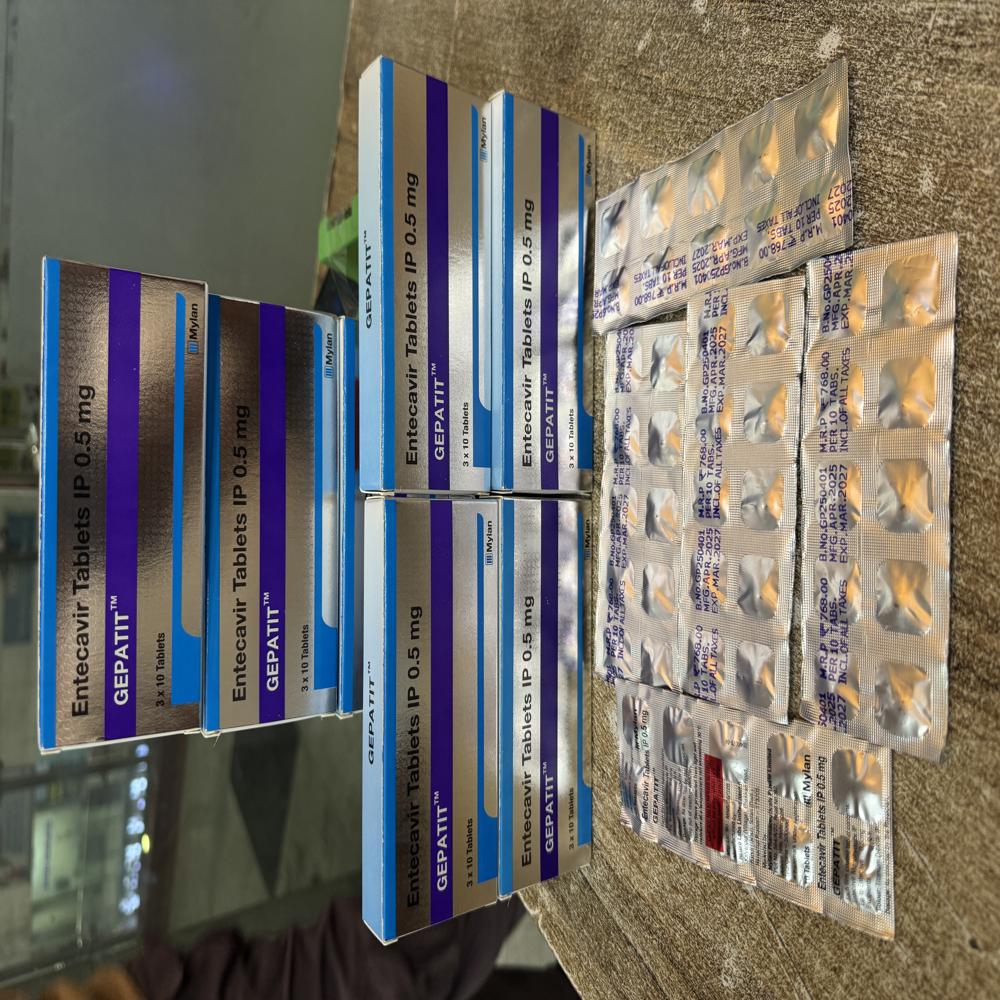
GEPATIT TABLETS 0.5 MG
Price 400.0 INR/ Piece
GEPATIT TABLETS 0.5 MG Specification
- Pacakaging (Quantity Per Box)
- 5 x 10 tablets
- Origin of Medicine
- India
- Dosage Form
- Tablets
- Drug Type
- General Medicines
- Physical Form
- Tablets
- Recommended For
- Adults
- Dosage
- As Per Instructions
- Dosage Guidelines
- As directed by a physician
- Suitable For
- Adults
- Storage Instructions
- Keep in a Cool & Dry Place
GEPATIT TABLETS 0.5 MG Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Piece
- FOB Port
- NEW DELHI
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Pieces Per Day
- Delivery Time
- 3 Days
- Sample Available
- No
- Sample Policy
- Contact us for information regarding our sample policy
- Packaging Details
- 1*30
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About GEPATIT TABLETS 0.5 MG





Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Hepatitis and Anti Viral Category
ENTEHEP-0.5 TABLETS
Price 758.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 3 Pieces
Drug Type : Other
Storage Instructions : ROOM TEMPERATURE
Origin of Medicine : INDIA
Suitable For : Women, Adults, Aged Person
EMTAF-B TABLETS
Price 809.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 2 Pieces
Drug Type : Other
Storage Instructions : ROOM TEMPERATURE
Origin of Medicine : INDIA
Suitable For : Women, Adults, Aged Person
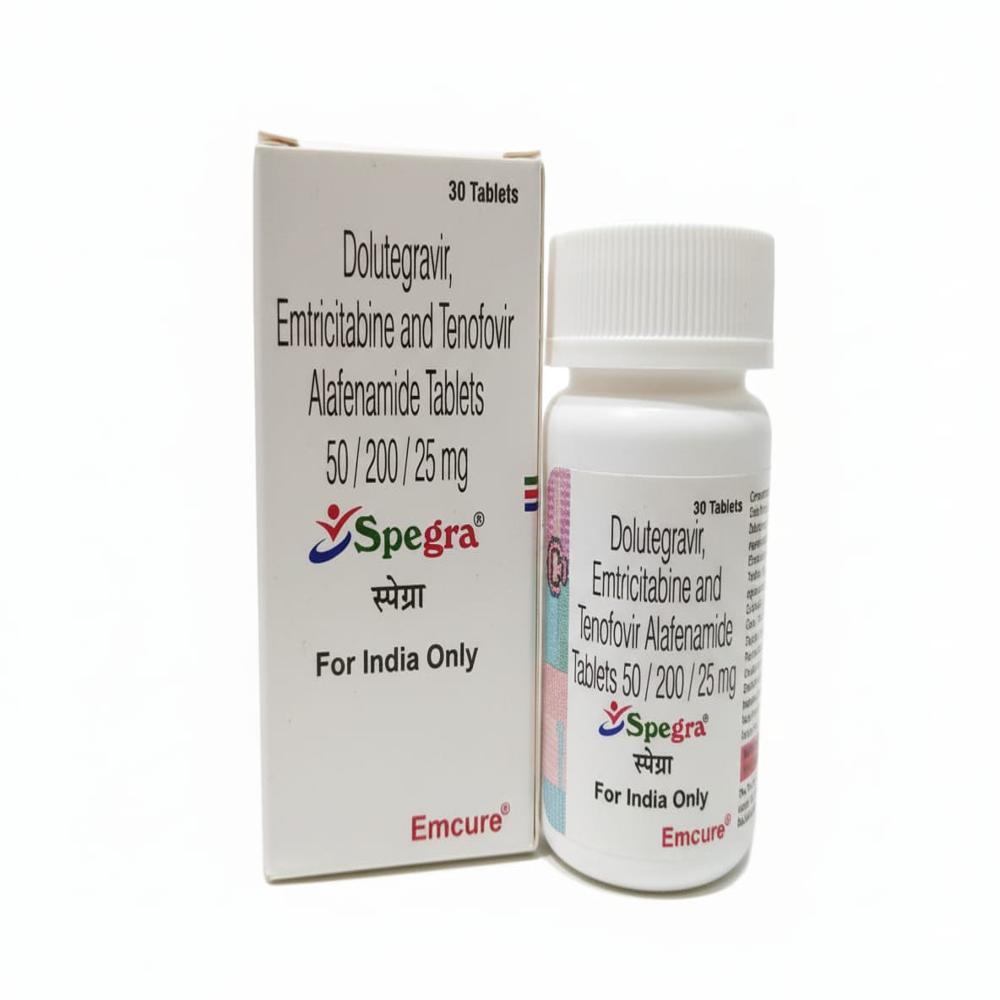
SPEGRA TABLETS
Price 2562.0 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 2 Pieces
Drug Type : Other
Storage Instructions : ROOM TEMPERATURE
Origin of Medicine : INDIA
Suitable For : Women, Adults, Aged Person
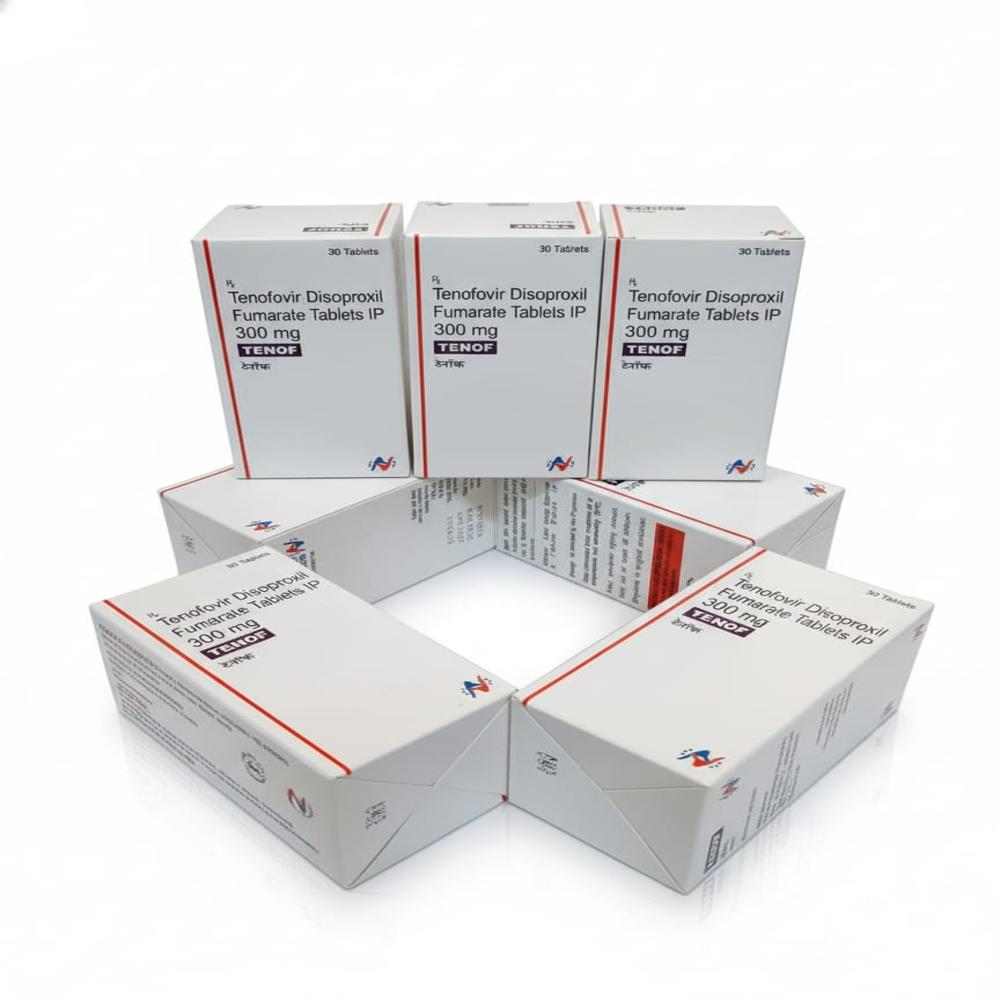
TENOF TABLETS 300 MG
Price 570.0 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Drug Type : Other
Storage Instructions : ROOM TEMPERATURE
Origin of Medicine : INDIA
Suitable For : Women, Adults, Aged Person

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese